Perimeter insulation:
Indispensable for energy efficiency and climate protection
Content
Introduction
1. What is perimeter insulation?
2. Advantages of Permeter insulation
3. Materials for perimeter insulation
4. planning and execution of perimeter insulation
5 The history of perimeter insulation
6. the largest manufacturers of perimeter insulation
7. ten essential practical tips for the successful use of perimeter insulation
8. the share of perimeter insulation in the energy efficiency of a house
9. perimeter insulation – A key to energy efficiency and climate protection
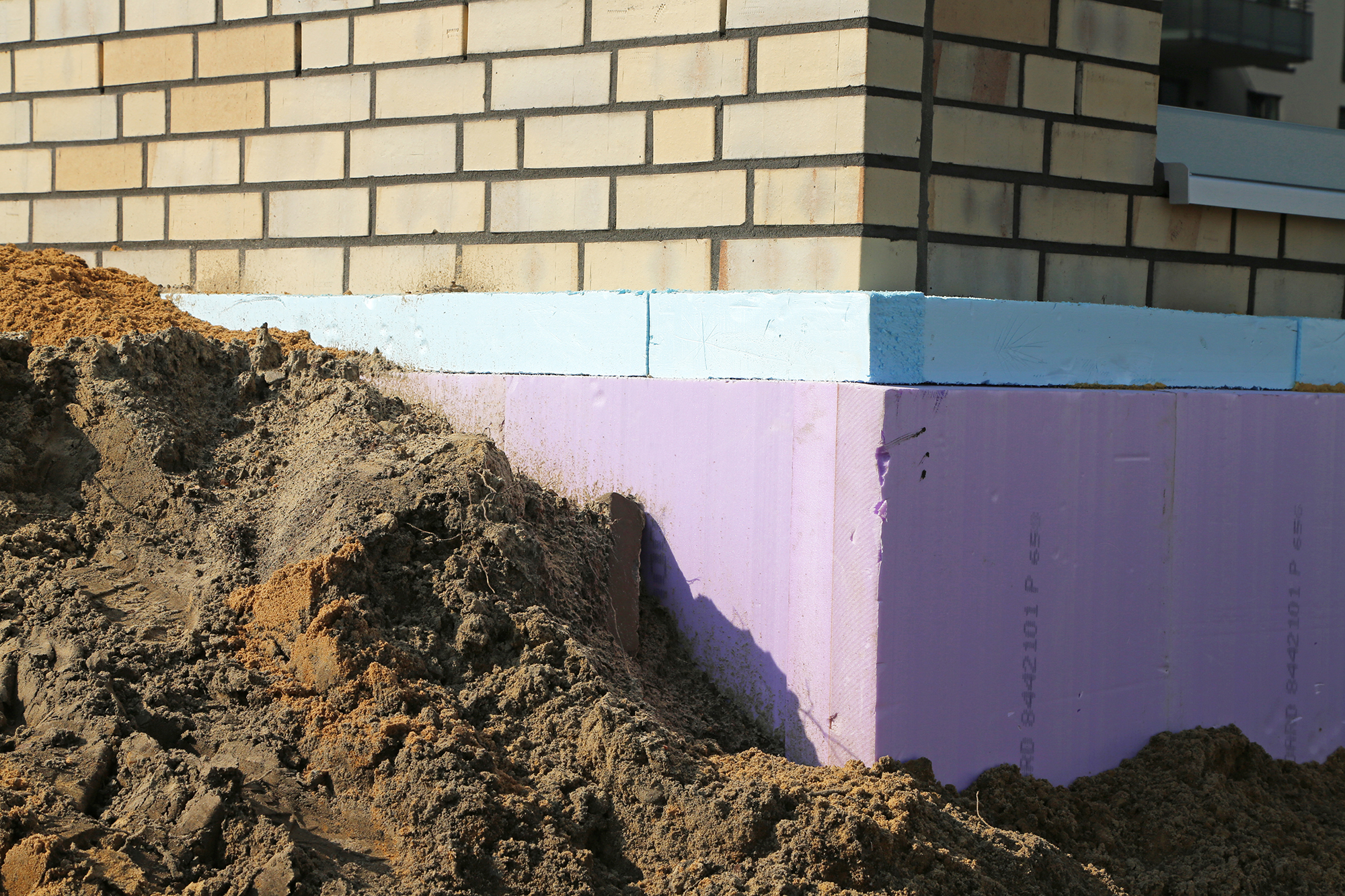

Perimeter insulation: Efficient thermal protection for buildings
Perimeter insulation is an efficient method of protecting buildings from heat loss and moisture. It is of particular importance for exterior basement walls, building components in contact with the ground and floor slabs. In this technical article you will learn everything you need to know about perimeter insulation, its advantages and the different materials that can be used for insulation.
1. what is perimeter insulation?
1.1 Definition and purpose
Perimeter insulation refers to the insulation of building components in contact with the ground, such as exterior basement walls and floor slabs. It prevents heat from the building from being released into the surrounding soil and at the same time protects against moisture penetration and cold from the ground.
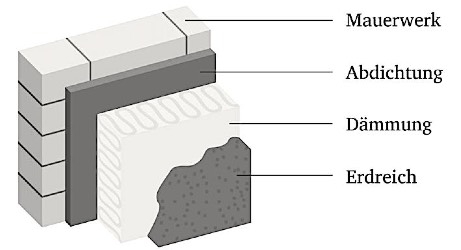
1.2 Areas of application
Perimeter insulation is used in particular for the following structures:
Residential and commercial buildings with basements
Underground garages
Swimming pools and wellness areas
Industrial and storage hall




2. advantages of perimeter insulation
2.1 Energy efficiency
By preventing heat loss, perimeter insulation helps to reduce the energy demand for heating and cooling. This leads to a reduction in operating costs and improved energy efficiency of the building.
2.2 Protection against moisture and mould growth
Properly executed perimeter insulation protects the building components in contact with the ground from moisture penetration. This prevents the development of moisture damage and mould, which can impair the building fabric and endanger the health of the occupants.
2.3 Improved quality of life
Thanks to the perimeter insulation, the basement area remains dry and warm. This allows for more comfortable use and expands the usable living space.
3. materials for perimeter insulation
3.1 Extruded polystyrene (XPS)
XPS is a widely used material for perimeter insulation. It is characterised by high compressive strength, moisture resistance and thermal insulation performance. XPS boards are easy to process and offer a durable solution for perimeter insulation.
3.2 Expanded polystyrene (EPS)
EPS is another common insulation material that is often used for perimeter insulation. It has similar properties to XPS, but is usually cheaper. However, EPS has a lower compressive strength, which can lead to deformation of the insulation boards under high loads.
3.3 Polyurethane (PUR/PIR)
Polyurethane insulation boards offer high thermal insulation performance with low material thickness. They are water-repellent and pressure-resistant, which makes them a suitable choice for perimeter insulation. However, PUR/PIR insulation boards are usually more expensive than XPS and EPS.

3.4 Mineral wool
Mineral wool, such as rock or glass wool, can also be used for perimeter insulation. It provides good thermal insulation and is non-combustible. However, it must be provided with an additional moisture barrier to effectively protect the building components in contact with the ground from penetrating moisture.
4. planning and execution of perimeter insulation
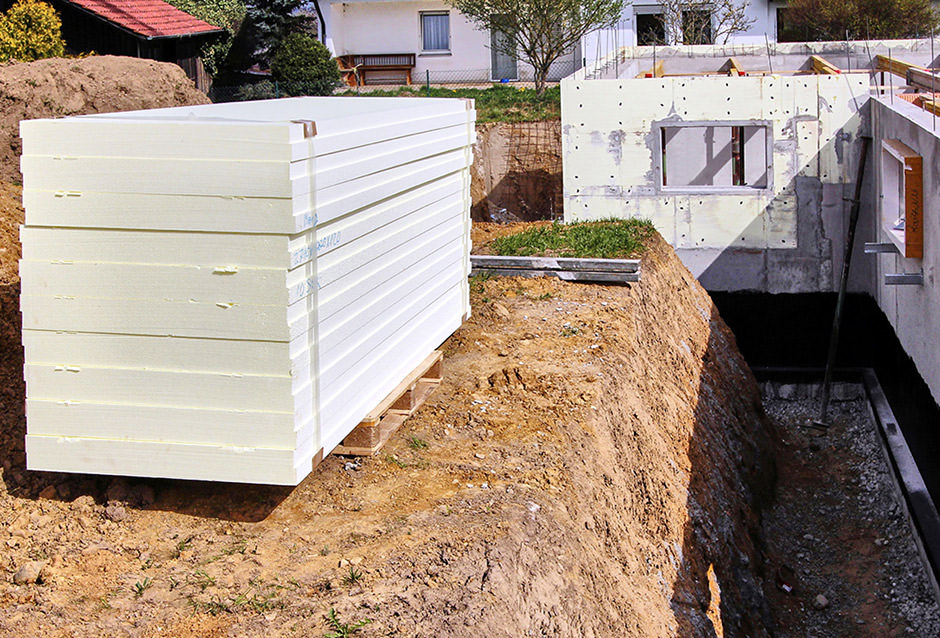

4.1 Requirements for the insulation
Choosing the right insulation material and thickness depends on various factors, such as the building physics requirements, the local conditions and the energy objectives of the building project. It is important to observe the relevant standards and guidelines to ensure professional execution of the perimeter insulation.
4.2 Waterproofing and drainage
Proper waterproofing and drainage are essential to effectively protect the building components in contact with the ground from moisture. This includes the use of suitable waterproofing membranes, drainage systems and Seepage layers that drain water away from the building and thus prevent damage.
4.3 Connection details and execution
The correct connection of the perimeter insulation to adjacent building components and the precise execution of the insulation work are decisive for the functionality and longevity of the insulation. This includes the gapless installation of the insulation boards, the avoidance of thermal bridges and the proper application of sealing membranes and waterproofing.
Conclusion
Perimeter insulation is an effective way to protect buildings from heat loss and moisture. It contributes to energy efficiency and living quality and prevents damage to the building fabric caused by moisture and mould. When planning and implementing perimeter insulation, the selection of suitable insulation material, compliance with the relevant standards and guidelines, and professional sealing and drainage are crucial. Through careful planning and implementation, building owners and planners can benefit from the advantages of efficient perimeter insulation and thus contribute to the creation of sustainable and comfortable living space.
"High-quality perimeter insulation is not only good for the wallet, but also for the environment. Because it reduces energy demand and thus CO2 emissions."
Helga, architect

5. the history of perimeter insulation:
Origin and development
Perimeter insulation has established itself over the years as an effective method to protect buildings from heat loss and moisture. In this article, we take a look at the history of perimeter insulation, its introduction and development, and the different techniques that have been used over time.

5.1 Origins of perimeter insulation
The beginnings of perimeter insulation date back to the 19th century.
5.1.1 Early beginnings
The first beginnings of perimeter insulation date back to the 19th century, when it was recognised that moisture and cold from the ground could penetrate buildings and lead to unpleasant living conditions. Even then, simple insulation and waterproofing measures were applied to combat these problems.

5.1.2 Scientific findings
In the 1920s and 1930s, the first scientific studies were conducted on heat transfer and moisture, which deepened the understanding of building physics. These findings laid the foundation for the development of insulation materials and insulation systems that were tailored to the special requirements of building components in contact with the ground.
5.2 Introduction of perimeter insulation

In the post-war period, and especially in the energy crisis of the 1970s, there was a growing awareness of how important good thermal insulation would be. The triumph of perimeter insulation was unstoppable.
5.2.1 Post-war period and energy crisis
The introduction of modern perimeter insulation took place in the post-war period, when the focus was on reconstruction and improving the quality of housing. In particular, the energy crisis of the 1970s led to an increased awareness of energy efficiency and thus greater interest in effective insulation methods.
5.2.2 Development of insulation materials
Parallel to the growing importance of energy efficiency, new insulation materials were developed in the 1960s and 1970s that were particularly suitable for perimeter insulation. These include extruded polystyrene (XPS) and expanded polystyrene (EPS), which are characterised by good thermal insulation performance, compressive strength and moisture resistance.
5.2.3 Distribution of perimeter insulation North America and Europe
Perimeter insulation was first introduced mainly in North America and Europe, where severe winter conditions and high heating costs drove the need for effective insulation solutions. In these regions, perimeter insulation quickly became an established method of keeping basements dry and comfortable.
5.2.4 Global distribution
As globalisation progressed and awareness of energy efficiency and sustainability increased, perimeter insulation spread to other parts of the world. Today, it is an integral part of building standards and energy requirements in many countries.
5.3 Current developments and future prospects
5.3.1 Further development of insulation materials
The continuous development of insulation materials makes it possible to make perimeter insulation even more efficient and sustainable. New materials such as polyurethane (PUR/PIR) or ecological alternatives such as wood fibre insulation boards offer improved thermal insulation performance and expand the range of choices for builders and planners.
Digitisation in construction brings new possibilities for perimeter insulation as well.
5.3.2 Digitisation and construction technology

Digitalisation and advances in construction technology make it possible to plan and implement perimeter insulation even more precisely and effectively. Computer-based simulations, Building Information Modelling (BIM) and modern manufacturing methods help to further improve the quality and durability of perimeter insulation.
The history of perimeter insulation has been marked by continuous developments and innovations due to a better understanding of building physics and the need for energy efficiency and sustainability in construction. From the first simple insulation and waterproofing measures in the 19th century to today's modern insulation systems, perimeter insulation has come a long way. The continuous development of materials and techniques suggests that perimeter insulation will continue to play an important role in the construction industry in the future.
6. the largest manufacturers of perimeter insulation





Origin and development
- BASF SE: BASF SE is one of the largest manufacturers of insulation materials and also offers a wide range of products for perimeter insulation.
- Saint-Gobain Isover: Saint-Gobain Isover is one of the world's leading manufacturers of insulation materials and offers a wide range of products for perimeter insulation.
- Rockwool: Rockwool is a well-known manufacturer of rock wool insulation materials and also offers products for perimeter insulation.
- Knauf Insulation: Knauf Insulation is a global manufacturer of insulation materials and offers a wide range of products for perimeter insulation.
- Kingspan Group: Kingspan Group is a global insulation manufacturer offering a wide range of perimeter insulation products.
These five manufacturers are among the largest and best-known producers of insulation materials and offer a wide range of products for perimeter insulation. Customers can choose from different materials and thicknesses to find the perfect solution for their requirements.
7. ten essential practical tips for the successful use of perimeter insulation
7.1 Material selection: Choose a suitable insulation material that meets the building physics requirements as well as the static and thermal requirements. Pay attention to the thermal conductivity value (lambda value) and the material resistance to moisture.
"Care is the top priority when working with perimeter insulation. Even small mistakes can have big consequences.
Peter, Site Manager

7.2 Joint clearance: Make sure that the insulation boards are joined together without joints to avoid thermal bridges and moisture problems. Also make sure that the boards are correctly aligned and fit together.
7.3 Waterproof connections: Ensure that the perimeter insulation is waterproofed by using suitable sealing tapes, membranes or compounds. Make sure that the joints between the boards and the foundation or basement wall are also sealed.
7.4 Protective layers: Integrate a suitable protective layer, such as drainage mats or perimeter insulation boards with integrated protection, to protect the insulation from mechanical damage and water.
7.5 Drainage: Ensure that a functioning drainage system is in place to quickly and efficiently channel excess water away from the perimeter insulation and foundation. This protects the building fabric from moisture and extends the life of the insulation.
7.6 Component connections: Make sure that the connections between perimeter insulation, foundation and adjacent building components are made carefully and professionally. This minimises thermal bridges and prevents moisture problems.
7.7 Compliance: Observe the applicable standards and guidelines for the installation of perimeter insulation to ensure optimum thermal protection and long-lasting functionality.
7.8 Professional assembly: Make sure that the perimeter insulation is installed by experienced professionals to avoid mistakes during installation and to ensure long-term effective thermal insulation. Professional installation is crucial for the performance and durability of the insulation.

Moisture is the greatest enemy of masonry.
7.9 Control and maintenance: Regularly check the condition of the perimeter insulation and carry out any necessary maintenance measures. In doing so, look out for signs of moisture, damage or wear and tear and rectify these at an early stage to avoid major problems.
7.10 Sustainable materials*: When choosing insulation materials, also consider ecological aspects and, if possible, opt for sustainable and environmentally friendly products. This can have a positive impact on the environmental balance of your building and contribute to higher energy efficiency in the long term.
* There are various ecological materials that can be used for perimeter insulation. Compared to conventional insulation materials, they have a lower environmental impact and are often more sustainable in production. Some examples of ecological insulation materials are:
Wood fibre insulation boards: These boards are made of renewable wood fibres and offer good thermal insulation as well as moisture regulation. They are open to diffusion and contribute to a pleasant indoor climate.
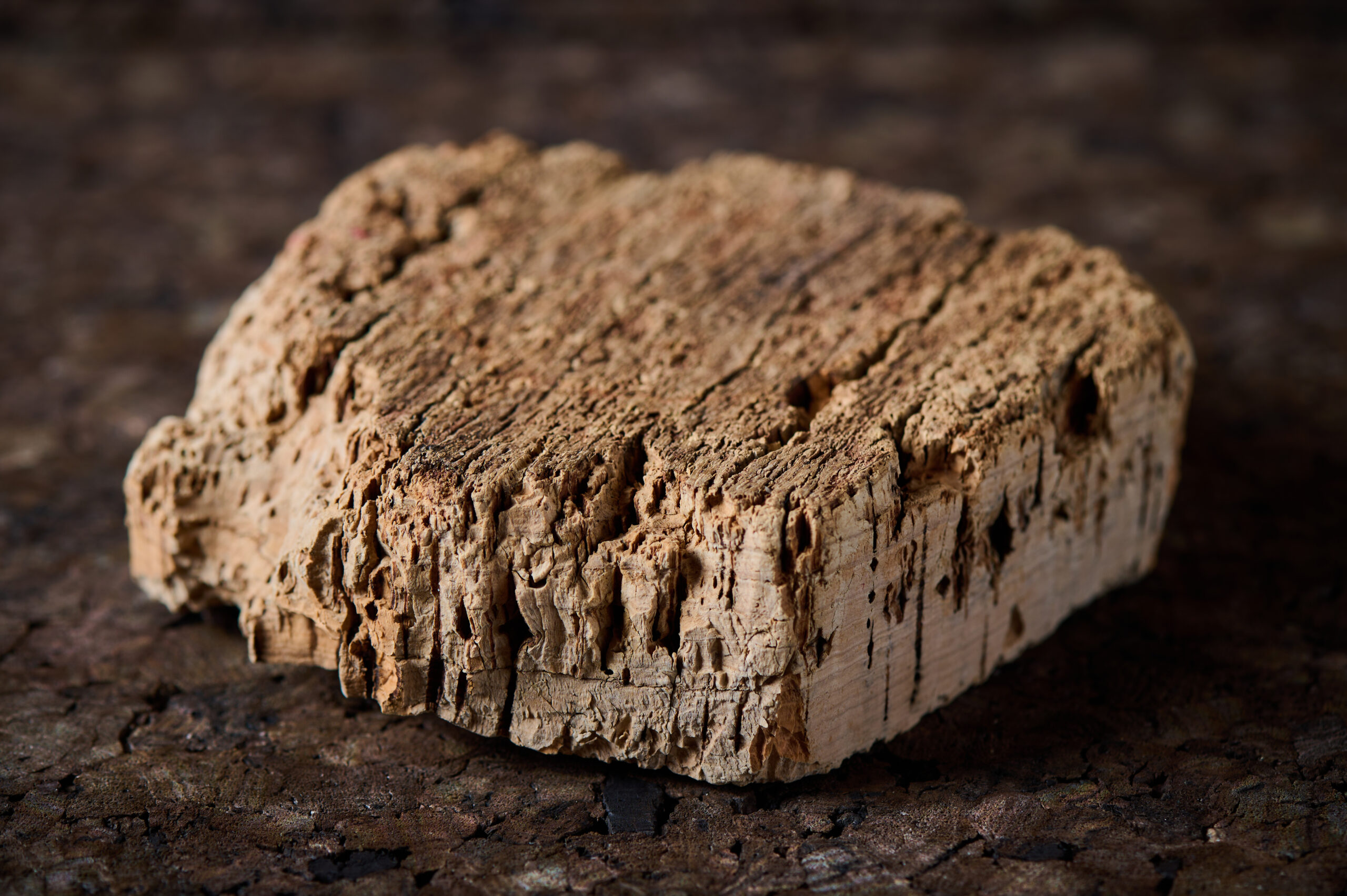

Cork insulation boards: Cork is a renewable raw material obtained from the bark of the cork oak. Cork insulation boards are water-repellent, resistant to mould and have good insulating properties.

Hemp insulation boards: Hemp is a fast-growing raw material and the insulation boards offer good thermal insulation as well as sound and heat protection. They are open to diffusion and can regulate moisture, contributing to a pleasant indoor climate.

Sheep wool insulation: Sheep's wool is a natural and renewable material that has good thermal insulation and soundproofing properties. It also regulates moisture and is resistant to mould.
Cellulose insulation: Cellulose is made from recycled newspaper and has good insulating properties. It can be used as blow-in insulation in the perimeter area and is environmentally friendly as well as resource-saving.
Perlite: Perlite is a naturally occurring volcanic rock that has good insulating properties due to its porous structure. It is insensitive to moisture and resistant to mould.
Calcium silicate boards: These boards are made of natural raw materials such as lime, sand and water. They are non-combustible, open to diffusion and moisture-regulating. Calcium silicate boards are particularly suitable for use in areas in contact with the ground.

8. the share of perimeter insulation in the energy efficiency of a house
The exact contribution of perimeter insulation to the energy efficiency of a house cannot be quantified across the board, as it depends on various factors. These include the climate, the construction method, the insulation materials and the quality of the workmanship.
Perimeter insulation refers to the insulation of the components of a building that are in contact with the ground, such as foundations, basement walls and floor slabs. Effective perimeter insulation can significantly reduce the heat loss of a building and thus make an important contribution to energy efficiency.
Basically, it can be said that perimeter insulation is an important component of a holistic insulation concept that includes both the building envelope (exterior walls, roof, windows) and components in contact with the ground. The energy efficiency of a house is influenced by the totality of the insulation measures, the efficiency of the heating system, the ventilation technology and the user behaviour.

With the right perimeter insulation, it's easy to stay cosy and warm.
What thermal values do the different perimeter insulation materials achieve?*
Perimeter insulation materials differ in their thermal conductivity, which is specified as the lambda value (λ). The lower the lambda value, the better the insulating effect of the material. Here are some common perimeter insulation materials and their approximate thermal conductivities:
Expanded polystyrene (EPS):
Lambda value: 0.032 to 0.045 W/(m-K)
EPS is widely used and offers good value for money. It is lightweight, easy to work with and moisture resistant.
Extruded polystyrene (XPS):
Lambda value: 0.030 to 0.038 W/(m-K)
XPS is even more pressure-resistant and moisture-resistant than EPS and is particularly suitable for applications where a high pressure load is expected.
Polyurethane (PU):
Lambda value: 0.022 to 0.030 W/(m-K)
PU insulation materials offer high thermal insulation performance with low material thickness, but are more expensive than EPS and XPS.
Mineral wool (glass wool or rock wool):
Lambda value: 0.032 to 0.040 W/(m-K)
Mineral wool provides good thermal insulation and is non-combustible. However, it is more susceptible to moisture and therefore not always the best choice for perimeter insulation unless it is combined with a special moisture protection layer.

Ecological and sustainable. Wood fibre insulation boards.
Wood fibre insulation boards:
Lambda value: 0.038 to 0.050 W/(m-K)
Wood fibre insulation boards are an ecological insulation material made from renewable raw materials. They provide good thermal insulation, are open to diffusion and can regulate moisture. However, they are usually less pressure-resistant than synthetic insulation materials.
Cellulose insulation:
Lambda value: 0.035 to 0.040 W/(m-K)
Cellulose insulation is made from recycled newspaper and can be used in board form or blown in loose. It provides good thermal insulation and is environmentally friendly, but is less suitable for perimeter insulation as it is susceptible to moisture.
Calcium silicate boards:
Lambda value: 0.050 to 0.070 W/(m-K)
Calcium silicate boards are a mineral insulation material used for interior applications to prevent condensation and mould growth. They can also be used for perimeter insulation, but have a higher thermal conductivity than other insulation materials and are less efficient.
Perlite:
Lambda value: 0.040 to 0.060 W/(m-K)
Perlite is a mineral insulation material extracted from volcanic rock. It is moisture-resistant, non-combustible and environmentally friendly. However, the thermal insulation performance of perlite is lower than most other perimeter insulation materials.
It is important to note that the actual insulation performance of a material depends on the quality and thickness of the insulation material, as well as on correct installation and processing. The choice of the right perimeter insulation material depends on various factors, such as climate, soil conditions, groundwater level, building physics requirements and budget. It is advisable to consult an expert to find the best solution for the project in question.
*What is the lambda value for perimeter insulation? What is measured?
The lambda value in perimeter insulation refers to the thermal conductivity of the insulation material used to insulate the building perimeter wall. The lambda value is a measure of the material's ability to conduct heat and indicates how much heat is conducted through the material.
A low lambda value means that the insulation material has a lower thermal conductivity and thus insulates better. A high lambda value, on the other hand, indicates that the material has a higher thermal conductivity and thus insulates worse.
When choosing insulation material for perimeter insulation, it is important to choose a material with the lowest possible lambda value to ensure effective thermal insulation. A low lambda value leads to lower heat losses and thus lower heating costs in winter and a cooler interior in summer.
In addition to lambda value, there are other parameters that need to be considered when choosing the right insulation material for perimeter insulation, such as the thickness and compressive strength of the material.
"Effective perimeter insulation is an important factor in minimising heat loss in winter and reducing the energy demand of a building.
Klaus, building contractor

9 Perimeter insulation - A key to energy efficiency and climate protection
Energy efficiency and climate protection are topics of great importance today. The building envelope plays a central role in this, as large amounts of energy can be saved here. Effective perimeter insulation is a key to energy efficiency and climate protection.
What is perimeter insulation?
Perimeter insulation refers to the insulation of the building's exterior walls in the ground. The aim is to minimise heat loss through the building's exterior wall while ensuring effective thermal insulation. A well-executed perimeter insulation offers numerous advantages such as the reduction of energy demand and thus energy costs, a higher quality of living due to a constant room temperature as well as a lower impact on the environment due to reduced CO2 emissions.
Energy efficiency needs in the building sector
The energy efficiency of buildings plays an important role in climate protection. This is because the energy refurbishment of buildings can help to reduce CO2 emissions and combat climate change. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, buildings contribute to about 40% of global energy consumption and about 30% of global CO2 emissions. Increasing the energy efficiency of buildings can therefore have a significant impact on climate change mitigation.

With the right perimeter insulation, heating costs are reduced and the climate is protected.
Energy efficiency through perimeter insulation
Effective perimeter insulation is an important measure to increase the energy efficiency of buildings. Well-done perimeter insulation can reduce the building's energy demand by up to 20%. This is because insulating the outer wall of the building can prevent heat from escaping outside and cold from entering the building. This can reduce the heating capacity of the building and thus reduce energy costs. Effective perimeter insulation also ensures a higher quality of living, as a constant room temperature is maintained.
Climate protection through perimeter insulation
Effective perimeter insulation can also make an important contribution to climate protection. Because by reducing the energy demand, CO2 emissions can be reduced. Effective perimeter insulation can help reduce CO2 emissions by up to 7 tonnes per year. This is particularly important because the building sector accounts for a significant share of global CO2 emissions.
Effective perimeter insulation is an important factor in increasing the energy efficiency and climate protection in the building sector. It contributes to reducing the energy demand of the building and thus also to lowering energy costs. At the same time, well-executed perimeter insulation can increase the quality of living and ensure a constant room temperature.
By reducing energy demand, CO2 emissions can also be reduced, which makes an important contribution to climate protection. Effective perimeter insulation can help reduce global CO2 emissions and thus combat climate change.
It is therefore important to consider perimeter insulation as an important component of energy efficiency and climate protection when planning and implementing building projects. Professionally executed perimeter insulation can not only save costs and increase living comfort, but also make an important contribution to combating climate change.

The 10 most important figures on the subject of perimeter insulation
1. 40%: Buildings are responsible for about 40% of the world's energy consumption.
2. 30%: Buildings contribute around 30% of global CO2 emissions.
3. 20%: Well-done perimeter insulation can reduce the building's energy demand by up to 20%.
4. 7 tons: Effective perimeter insulation can reduce CO2 emissions by up to 7 tonnes per year.
5. 0.035 W/(mK): The recommended thermal conductivity value (lambda value) for insulation materials in perimeter insulation.
6. 50 years: The service life of effective perimeter insulation is at least 50 years.
7. 10 cm: The minimum thickness of perimeter insulation to ensure adequate thermal protection.
8. 3,000 euros: The average cost of perimeter insulation is around 3,000 euros per running metre.
9. 50 cm: The recommended distance between the perimeter insulation and the ground to ensure adequate ventilation and drainage.
10. 70 kPa:The minimum compressive strength of the insulation material for perimeter insulation to ensure sufficient stability.
These figures illustrate the importance of effective perimeter insulation for energy efficiency and climate protection in the building sector. Well-done perimeter insulation can not only reduce the energy demand of the building and increase the quality of living, but also make an important contribution to reducing CO2 emissions.

